Selection Guide:
When designing and choosing a standoff for your next application, first determine whether a standoff, swage standoff, or spacer will be best for your application.
If you’ve decided a standoff will work best for your needs, the below guide will provide the common information needed for finding the right standoff.
If you still have questions, feel free to contact us and we’ll be happy to guide you in the right direction:
Know what you're looking for already?
Step 1 - Spacer Type
It is easiest to think of standoffs as 3 separate sections; the two threaded ends and the main body. Because of this, standoffs are divided into a few different styles and named after the type of threads on each end.
Female-Female Standoffs
These are also referred to as a threaded spacer and come with female threads on both ends of the part. This allows for a screw or male standoff to be installed on either side. In shorter lengths, standoffs will be threaded through the entire part, where longer standoffs are threaded to a minimum thread depth.
Male-Female Standoffs
These have one end with a male thread and the other end has a female thread. These are excellent for use when stacking circuit boards as each male thread can be installed into the mating part’s female thread. This quickly reduces the number of fasteners needed in the assembly while also reducing installation time.
Male-Male Standoffs
This has male threads on both ends and is used to connect 2 female threaded components. These are also commonly utilized as thread adapters to convert a female thread to a male thread. Male ends can be the same or a different thread for a wider range of applications.
Step 2 - Thread Size
Standoffs are readily available in all common thread sizes, in both inch and metric series. While most commonly found with each end having the same size thread, different thread sizes are available upon request.
Step 3 - Body Length
As standoffs are commonly used to separate 2 components, the body of the standoff is what will separate the components. All standoffs come in a wide range of length options. Parts are machined to a tight tolerance of +/-0.005” (+/-0.13mm) for a secure and consistent fit. Custom lengths and tolerances are available upon request.
| Inch Standoffs | Standard Lengths Available |
|---|---|
| 1/8" Standoffs | 1/8" - 1" |
| 3/16" Standoffs | 1/8" - 2" |
| 1/4" Standoffs | 1/8" - 10" |
| 5/16" Standoffs | 1/8" - 10" |
| 3/8" Standoffs | 1/8" - 10" |
| 1/2" Standoffs | 1/8" - 10" |
| 5/8" Standoffs | 1/8" - 10" |
| Metric Standoffs | Standard Lengths Available |
|---|---|
| 4.5mm Standoffs | 3mm - 51mm |
| 6mm Standoffs | 3mm - 51mm |
| 8mm Standoffs | 3mm - 51mm |
| 10mm Standoffs | 3mm - 51mm |
| 13mm Standoffs | 3mm - 51mm |
Step 4 - Outer Diameter (OD)
All thread combinations have multiple, standard outside diameters to choose from to give the exact form, fit and function you are looking for.
-
A Larger OD creates a thicker standoff and is an easy way to add strength and rigidity. The added wall thickness will resist bending or warping during installation, but also adds bearing surface to prevent damage on soft and delicate materials.
-
Smaller OD’s result in a thin standoff and are perfect when space and weight are the primary concern. Choosing a smaller OD will decrease the footprint of the spacer. This gives more room for other components and reduces part weight.
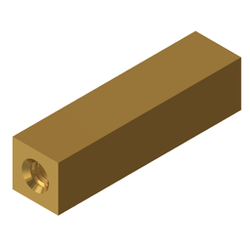
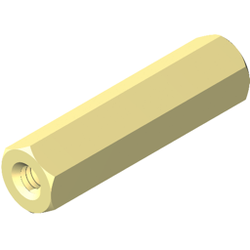
Step 5 - Profile
Hex Standoffs are often selected when installed with a wrench or pliers as the “Hex Flats” provide a surface to grip onto during installation. Round or square profiles can also be used and provide a clean, distinctive appearance. When using multiple standoffs in the same assembly, some manufacturers will select different profiles on similar parts to provide a visual difference on the assembly line.
Step 6 - Material & Plating Options
When deciding on a material and plating/finish, there are many properties that can be considered. The most common ones include Corrosion and Rust Resistance, Magnetism, Electrical Conductivity, Strength to Weight Properties, Color, and Cost. Review the chart below to see which standard material has the right properties for your application’s environment. For an explanation of RoHS, Conflict Minerals, WEEE and REACH visit our Technical section.
| Materials | Corrosion Resistance | Magnetic | Electrical Conductor | Strength to Weight | Color | Plates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High | Slightly | Yes - Poor | Above Average | Grey | Available |
| Steel | Low | Strongly | Yes - Poor | Average | Grey | Available |
| Aluminum | Average | No | Yes - Average | Very Above Average | Grey | Available |
| Brass | High | No | Yes - Below Average | Average | Yellow | Available |
| Nylon | High | No | No | Average | White and can be dyed to other colors | No |
For an explanation of RoHS, Conflict Minerals, WEEE and REACH visit our Technical Section.
Have a Question About Precision Standoff Hardware?
Electronic components are unique and guides can’t always answer everything. Please fill out this form and we will get right back to you.